Answer:
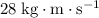 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
The impulse on an object is equal to the change in momentum.
By the conservation of momentum, the total momentum of this system will stay unchanged. In other words, the sum of the change in the momentum of the wall and the projectile will be
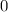 :
:
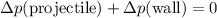 .
.
Rearrange to obtain:
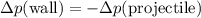 .
.
The change in the momentum of the projectile is:
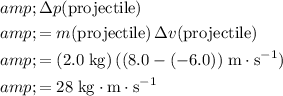 .
.
The change in the momentum of the wall would then be:
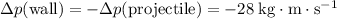 .
.
Thus, the magnitude of the impulse on the wall would be
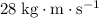 .
.