The temperature that the balloon must reach to expand to a volume of 4.6 L is 596 Kelvin.
To solve this problem, we can use Charles' Law, which states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature, as long as a constant pressure is maintained.
The mathematical formula for Charles' Law is:
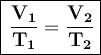
Where:
- V₁ is the initial volume
- T₁ is the initial temperature
- V₂ is the final volume
- T₂ is the final temperature
In this case, we have the following values:
- V₁ = 2.3 L
- T₁ = 25 °C + 273 = 298 K
- V₂ = 4.6 L
- T₂ = ?
We can rearrange the Charles Law formula to solve for T₂:
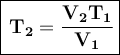
Where:
- V₁ is the initial volume
- T₁ is the initial temperature
- V₂ is the final volume
- T₂ is the final temperature
Substituting the known values:
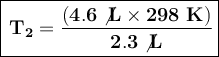

The temperature that the balloon must reach to expand to a volume of 4.6 L is 596 Kelvin.
NOTE: The temperature in degrees Celsius (°C), in these types of exercises are always converted into Kelvin (K).