Answer:
The electrochemical equivalent of copper, Cu, is 3.29015544 × 10⁻⁷ g/C
Step-by-step explanation:
The given parameters are;
The element for which the electrochemical equivalent is sought = Copper
The atomic mass of copper = 63.5
The electrochemical equivalent, 'Z', of an element or a substance is the mass, 'm', of the element or substance deposited by one coulomb of electricity, which is equivalent to a 1 ampere current flowing for a period of 1 second
Mathematically, we have;
m = Z·I·t = Z·Q
We have;
Cu²⁺ (aq) + 2·e⁻ → Cu
Therefore, one mole of Cu, is deposited by 2 moles of electrons
The charge carried one mole of electrons = 1 Faraday = 96500 C
∴ The charge carried two moles of electrons, Q = 2 × 96500 C = 193,000 C
Given that the mass of an atom of Cu = 63.5 a.m.u., the mass of one mole of Cu, m = 63.5 g
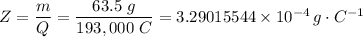
∴ Z = 3.29015544 × 10⁻⁴ g/C = 3.29015544 × 10⁻⁷ g/C
The electrochemical equivalent of copper, Cu, is Z = 3.29015544 × 10⁻⁷ g/C