Final Answer:
The equilibrium constant expression for the reaction is given by:
![\[ K_c = \frac{[\text{Products}]}{[\text{Reactants}]} = 78 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/e5fw1urw23fy0r4gomswlvue3v80mk6905.png)
Step-by-step explanation:
In the given question, the equilibrium constant (\(K_c\)) is stated to be 78. The equilibrium constant expression for a reaction is defined as the ratio of the concentrations of products to reactants, each raised to the power of their respective coefficients in the balanced chemical equation. In mathematical terms, it is represented as:
![\[ K_c = ([C]^c [D]^d)/([A]^a [B]^b) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/one4v5bzo7z3zhz0htbjkkewuwhw85sgom.png)
where
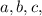 and
and
 are the coefficients of the balanced chemical equation
are the coefficients of the balanced chemical equation
 The square brackets denote molar concentrations.
The square brackets denote molar concentrations.
In the given context, the equilibrium constant is specified as 78. This implies that, at equilibrium, the ratio of the concentrations of products to reactants is equal to 78. It's important to note that the value of the equilibrium constant is independent of the initial concentrations and depends solely on the stoichiometry of the reaction.
To elaborate further, if the reaction is represented as
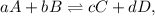 the equilibrium constant expression would be
the equilibrium constant expression would be
![\(K_c = ([C]^c [D]^d)/([A]^a [B]^b) = 78\).](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/a2683e8zxpbq0g5kpivd680hhpmq8en2o1.png) This mathematical relationship encapsulates the balanced nature of the reaction at equilibrium. The magnitude o
This mathematical relationship encapsulates the balanced nature of the reaction at equilibrium. The magnitude o
 provides insights into the position of the equilibrium—larger values indicating a shift toward the products, and smaller values favoring the reactants.
provides insights into the position of the equilibrium—larger values indicating a shift toward the products, and smaller values favoring the reactants.