To determine the probability of rolling two even numbers, we need to find the favorable outcomes (outcomes with two even numbers) and divide it by the total number of possible outcomes.
The possible outcomes when rolling two dice are:
(1,1), (1,2), (1,3), (1,4), (1,5), (1,6)
(2,1), (2,2), (2,3), (2,4), (2,5), (2,6)
(3,1), (3,2), (3,3), (3,4), (3,5), (3,6)
(4,1), (4,2), (4,3), (4,4), (4,5), (4,6)
(5,1), (5,2), (5,3), (5,4), (5,5), (5,6)
(6,1), (6,2), (6,3), (6,4), (6,5), (6,6)
Out of these, the favorable outcomes (outcomes with two even numbers) are:
(2,2), (2,4), (2,6), (4,2), (4,4), (4,6), (6,2), (6,4), (6,6)
Thus, there are 9 favorable outcomes.
The total number of possible outcomes is 36 (since each die has 6 possible outcomes).
Therefore, the probability of rolling 2 even numbers is:
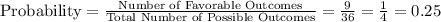
Hence, the probability of rolling 2 even numbers is 0.25 or 1/4.