Answer:
The last option, t=4.52 s.
Step-by-step explanation:
The following information will help you tackle any projectile motion problem (assuming there is zero air friction), so please read carefully.
This projectile motion problem is solvable with some basic knowledge of projectile physics and the use of the 4 kinematic equations that are written below.
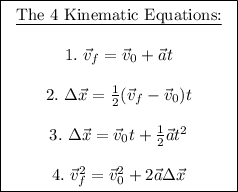
Things to note about the above kinematic equations:
In order to use the above equations, two things MUST be true.
i. Acceleration is constant.
ii. You must know at least three pieces of information.
When dealing with 2-D motion, NEVER mix horizontal and vertical components together in the same equation.
Tackling Projectile Motion Problems:
To tackle any projectile motion problem, you will have to split components up into x and y. I personally like to make a table which you will see later as I am solving the question.
Things that are true for all 2-D projectile motion problems:

The horizontal component of velocity will be the same throughout the projectiles flight while the vertical component of velocity is variable (always changing). The horizontal component of acceleration will always be zero while the vertical component of acceleration will be the acceleration due to gravity. These things are crucial to understand when dealing with projectile motion problems.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Given:
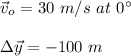
Find:
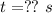
(1) - Splitting up what we know into it horz. and vert. components
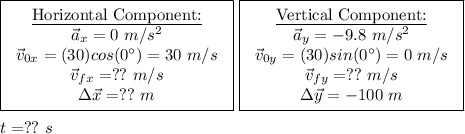
(2) - As you can see from the table above we know three pieces of information for the vertical components. I will use equation 3 to solve for the time, t
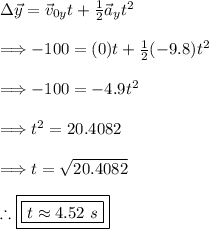
Thus, it takes about 4.52 seconds for the projectile to hit the ground.