To find P(N = k), we need to calculate the probability that the first 4 rolls are not larger than 4, and the kth roll is larger than 4.
The probability that any given roll is larger than 4 is 2/6 = 1/3. Therefore, the probability that the first k-1 rolls are not larger than 4 and the kth roll is larger than 4 is
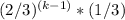 .
.
So,
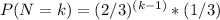 .
.
To find how many trials we will need on average, we can use the formula for the expected value of a geometric distribution: E(N) = 1/p, where p is the probability of success (in this case, rolling a number larger than 4).
So, p = 1/3, and E(N) = 1/p = 3. Therefore, on average, we will need 3 trials to observe a number larger than 4.
To know more about probability refer here