Answer:
Keq = 0.013
Step-by-step explanation:
Keq is the ratio of the concentrations of the products to the concentration of the reactants.
For any reaction aA+bB->cC+dD (a,b,c,d are coefficients),
![K_(eq)=([C]^c[D]^d)/([A]^a[B]^b)](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/college/s5xv4yqv72ei48sg680ewf4bgym8owcr69.png) .
.
Furthermore, pure solids and liquids are omitted from these Keq expressions; the only things included in Keq expressions are aqueous or gaseous substances.
Since the coefficients for all reactants and products in the given reaction is 1 and water is omitted because it is a pure liquid,
![K_(eq)=([F^-][H_3O^+])/([HF])](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/college/y1at62hak09vxu1lbf55askadpt09mdn7b.png) .
.
Plugging in the concentrations gives
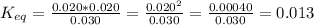 .
.