Answer:
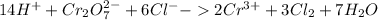
Step-by-step explanation:
Step 1:
First, figure out what is oxidized and reduced in the reaction.
The Cl- is oxidized into Cl2 because Cl in Cl- has oxidation state of -1 and Cl in Cl2 has oxidation state of 0.
Oxygen almost always has oxidation state of -2, so oxidation state of Cr in dichromate is 2x + 7*-2 = -2, where oxidation of Cr is x. Solving the equation gives 2x - 14 = -2, then 2x = 12, then x = 6, so Cr has oxidation state of +6 in dichromate. Since Cr3+ has oxidation state of +3, Cr is reduced.
Step 2:
Split redox reaction into two half reactions, one reaction will have oxidation and the other will have reduction. The following half reactions are shown below:
Reduction:
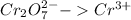
Oxidation:
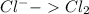
Step 3:
Balance the Cr and Cl atoms in the half reactions:
Reduction:
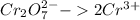
Oxidation:

Step 4:
Balance the number of oxygen atoms in the half reactions using water:
Reduction:
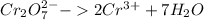
Oxidation:

Step 5:
Balance the number of hydrogen atoms in the half reactions using H+ because the redox reaction takes place in an acidic solution:
Reduction:
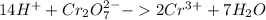
Oxidation:

Step 6:
Balance the charges in the half reaction using electrons:
Reduction:
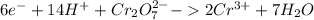
Oxidation:
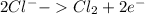
Step 7:
To combine the balanced half reactions, the number of free electrons produced through oxidation must equal the number of free electrons used up through reduction. This is done by multiplying the half reactions by different amounts:
Reduction:
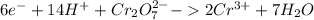
Oxidation:
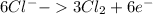
Step 8:
Now when the balanced half reactions are combined, the electrons on both sides will cancel out, giving us the fully balanced redox reaction:
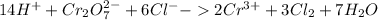
This way of balancing redox reactions is called the ion-electron method. I would recommend googling it and learning it well. Redox reactions in basic solutions have one or two extra steps compared to acidic solutions.