Final Answer:
The equilibrium constant (KC) for the given reaction
![2HF(aq) + C2O4^2-(aq) ⇄ 2F^-(aq) + H2C2O4(aq) is \(K_C = \frac{{[F^-]^2 \cdot [H_2C_2O_4]}}{{[HF]^2 \cdot [C_2O_4^(2-)]}}\),](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/d030exujja8gamfijup7anbvsxnthxvn4r.png) where the concentrations are determined by the given equilibria
where the concentrations are determined by the given equilibria
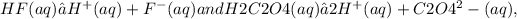 with equilibrium constants
with equilibrium constants
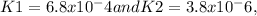 respectively.
respectively.
Step-by-step explanation:
To determine KC for the reaction, we can use the information provided about the equilibria involved. The given reaction involves the dissociation of HF and H2C2O4. Using the equilibrium constants (K1 and K2), we can express the concentrations of the various species at equilibrium. The equilibrium constant for the overall reaction (KC) is then determined by the ratio of the concentrations of the products to the concentrations of the reactants.
The expression for KC is derived from the stoichiometry of the reaction, and it involves squaring the concentration of fluoride ions
![([F^-])](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/i9gff2btv4sgasb9ztofzr6poaw042w002.png) and the concentration of H2C2O4, while dividing by the squared concentration of HF and the concentration of oxalate ions
and the concentration of H2C2O4, while dividing by the squared concentration of HF and the concentration of oxalate ions
![([C2O4^2-])](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/oejj5fvzz8e3if721wl8qddya3bdzlh7mm.png) . Substituting the values of K1 and K2 into the expression allows for the calculation of KC.
. Substituting the values of K1 and K2 into the expression allows for the calculation of KC.
Performing the calculations,
![\(K_C = \frac{{(6.8x10^(-4))^2 \cdot [H_2C_2O_4]}}{{(3.8x10^(-6))^2 \cdot [HF] \cdot [C_2O_4^(2-)]}}\),](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/2zdr1pvgwozmx3ko8g32sf87a4muiim5yf.png) will give the final numerical value for KC. This approach ensures that the equilibrium concentrations of all relevant species are considered, providing a comprehensive understanding of the reaction's equilibrium position.
will give the final numerical value for KC. This approach ensures that the equilibrium concentrations of all relevant species are considered, providing a comprehensive understanding of the reaction's equilibrium position.