Final answer:
An empirical formula is the simplest representation of a compound's composition, written as the lowest whole-number ratio of its elements. It is used for comparison and chemical analysis but does not indicate the actual number of atoms in the compound.
Step-by-step explanation:
An empirical formula represents the simplest whole-number ratio of elements in a compound. It does not show the actual number of atoms but rather the ratio that reflects the proportion of the elements present. For example, the molecular formula for glucose is
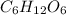 , but when each subscript is divided by the smallest common divisor, 6, we get the empirical formula
, but when each subscript is divided by the smallest common divisor, 6, we get the empirical formula
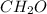 , indicating a ratio of 1 Carbon to 2 Hydrogens to 1 Oxygen. This is useful in chemistry because it provides insights into the composition of compounds and allows for the comparison of different substances.
, indicating a ratio of 1 Carbon to 2 Hydrogens to 1 Oxygen. This is useful in chemistry because it provides insights into the composition of compounds and allows for the comparison of different substances.
Chemists calculate the empirical formula of a compound by first determining the percentage composition of each element and then converting these percentages into a mole ratio. The empirical formula is instrumental in understanding chemical reactions and properties of substances because it reflects the simplest form of the compound's composition.