Answer:
290 L (3 s.f.)
Step-by-step explanation:
First, balance the equation:
2H₂(g) + O₂(g) → 2H₂O(g)
Now, calculate the number of moles in the given mass of oxygen gas (O₂) by using the formula:
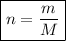
where:
- n is the number of moles.
- m is the mass (in grams).
- M is the molar mass of the material.
The molar mass of O₂ is 31.999 g/mol.
Therefore, the number of moles in 155 g of oxygen gas is:
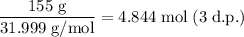
We have been told that hydrogen is in excess, which means we can assume that all the moles of oxygen will react.
The mole ratio between oxygen gas and water is 1 : 2. This means that the reaction will produce twice as many moles of water as moles of oxygen. Therefore, the number of moles of water is:
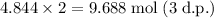
To determine how many liters of water can be made at 0.850 atm and 310 K, use the ideal gas law equation.
Ideal Gas Law
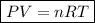
where:
- P is the pressure measured in atmosphere (atm).
- V is the volume measured in liters (L).
- n is the number of moles.
- R is the ideal gas constant (0.082057366080960 atm L mol⁻¹ K⁻¹).
- T is the temperature measured in kelvin (K).
Rearrange the formula to isolate V:
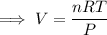
Substitute the values into the formula and solve for V:

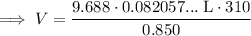
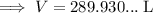
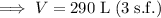
Therefore, 290 liters of water (to three significant figures) can be made from 155 grams of oxygen gas and an excess of hydrogen at 0.850 atm and 310 K.