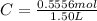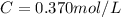Molarity also known as molar concentration is a measurement of moles of a solute compared to the total volume of the solution.
Some general formulas to help us answer this question:
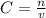
- C= molar concentration/molarity (M or mol/L)
- v= volume of solution (measured in L)
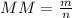
- MM = molar mass (g/mol)
- m= mass (g)
- n = moles
To calculate the molarity we must first find moles. This is possible given the mass of solute (glucose) and the molar mass of glucose.
Rearranging the second equation we get :
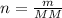
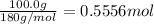
Now we can use
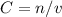 to calculate molarity
to calculate molarity