Answer: Newton's Second law of motion says that: the "Rate of change of momentum of a body is directly proportional to the applied force on the body."
Explanation: Let The force applied on a body be 'F', and the change in momentum of the body in 't' time is 'p' then according to the above statement:
1. F∝
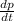
2. F=k.
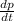 (where k is the proportionality constant)
(where k is the proportionality constant)
3. F=k.
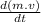 (momentum = velocity x mass)
(momentum = velocity x mass)
4. F= k.(m.
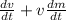 ) (separation formula of derivation)
) (separation formula of derivation)
5. F=
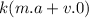 (at low-speed mass does not vary with time so,
(at low-speed mass does not vary with time so,
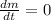 )
)
6. F= k.m.a (for unit mass to produce 1 m/
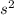 acceleration 1-newton force is required hence in SI units: k=1 )
acceleration 1-newton force is required hence in SI units: k=1 )
7. F=m.a (this is the equation for the second law of motion)