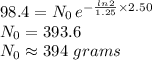Answer:
394 grams initially in the rock
Half Life:
The activity of a radioactive isotope is measured by the isotope's half-life. Half-life is the time it takes for half of the nuclei in a radioactive sample to undergo radioactive decay. Radioisotopes can have half-lives from fractions of a second, to billions of years.
The formula for exponential decay, studied in mathematics, can be used to describe the amount of undecayed radioisotopes present after a certain amount of time:

- Nt = amount of undecayed radioisotopes present after a time t
- N₀ = initial amount of radioisotopes
When one half-life (denoted by
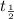 ) has elapsed, half the radioisotopes would have undergone radioactive decay. Hence after one half-life:
) has elapsed, half the radioisotopes would have undergone radioactive decay. Hence after one half-life:
Nt = N₀/2, and we can write this equation as:
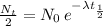 . Isolating λ to one side, we are left with the formula for the decay constant:
. Isolating λ to one side, we are left with the formula for the decay constant:
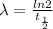
- λ = decay constant
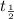 = half-life
= half-life
Therefore, if potassium-40 decays with a half-life of 1.25 billion:
- t = 2.50
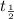 = 1.25
= 1.25
We can calculate decay constant:
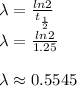
Hence: