Answer:
3.27 atm (3 s.f.)
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the pressure of the helium gas, we can use the Ideal Gas Law.
Ideal Gas Law
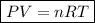
where:
- P is the pressure measured in atmosphere (atm).
- V is the volume measured in liters (L).
- n is the number of moles.
- R is the ideal gas constant (0.082057366080960 atm L mol⁻¹ K⁻¹).
- T is the temperature measured in kelvin (K).
The values to substitute into the equation are:
- V = 3.32 L
- n = 0.521 mol
- R = 0.082057366080960 atm L mol⁻¹ K⁻¹
- T = 254 K
Rearrange the formula to isolate P:
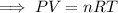
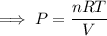
Substitute the values into the formula and solve for P:
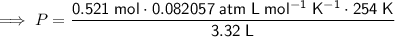
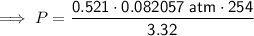
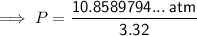
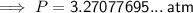
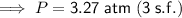
Therefore, the pressure of the helium gas is 3.27 atm (to three significant figures) when it occupies a volume of 3.32 L at 254 K.