Answer:
87.33 kPa (2 d.p.)
Step-by-step explanation:
To solve this problem, use the combined gas law.
Combined Gas Law
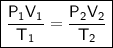
where:
- P₁ is the initial pressure.
- V₁ is the initial volume.
- T₁ is the initial temperature (in kelvin).
- P₂ is the final pressure.
- V₂ is the final volume.
- T₂ is the final temperature (in kelvin).
As we want to find the final pressure, rearrange the formula to isolate P₂:
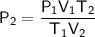
As the temperatures have been given in Celsius, we need to first convert the temperatures from Celsius to kelvin by adding 273.15:
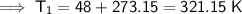
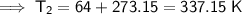
The given values are:
- P₁ = 108 kPa
- V₁ = 0.952 L
- T₁ = 321.15 K
- V₂ = 1.236 L
- T₂ = 337.15 K
Substitute the values into the formula and solve for P₂:
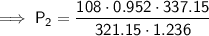
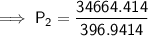
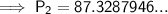
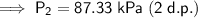
Therefore, the final pressure of the gas is 87.33 kPa (2 d.p.).