Answer: The activation energy Ea for this reaction is 22689.8 J/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
According to Arrhenius equation with change in temperature, the formula is as follows.
![ln (k_(2))/(k_(1)) = (-E_(a))/(R)[(1)/(T_(2)) - (1)/(T_(1))]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/y95oqc16xhfspirxcw3imk40ehtx0adjz2.png)
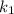 = rate constant at temperature
= rate constant at temperature
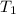 =
=

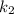 = rate constant at temperature
= rate constant at temperature
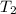 =
=

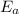 = activation energy = ?
= activation energy = ?
R= gas constant = 8.314 J/kmol
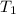 = temperature =
= temperature =
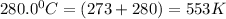
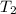 = temperature =
= temperature =
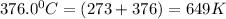
Putting in the values ::
![ln (4.8* 10^8)/(2.3* 10^8) = (-E_(a))/(8.314)[(1)/(649) - (1)/(553)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/o2lfdljr9nfxhamd1igelbzshpd4tv1mpa.png)
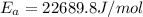
The activation energy Ea for this reaction is 22689.8 J/mol