The car must produce a power of 6760 W, or about 9.06 hp, to maintain its speed against the drag force. On an incline with a 6° angle, the new power required is approximately 61412 W or 82.3 hp to maintain the same speed.
Given:
m = 2050 kg
v = 26 m/s
Drag force,
 = 260 N
= 260 N
(a) The power P required to maintain a constant speed is given by the product of force and velocity:
![\[ P = F \cdot v \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/h7v5pvbh0ollzbijvtceyja7s39ywc82z9.png)
where F is the force applied, and v is the velocity.
P = 260 x 26 = 6760 W
(b) To convert the power from watts to horsepower, you can use the conversion factor:
1 hp = 746 W
![\[ P_{\text{HP}} = (260 \, \cdot 26 \, )/(746 \ ) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/c0qeffdo9hk84d1aaz4xp86pywpaxt3mpi.png) = 9.06 hp
= 9.06 hp
(c) When the car encounters an incline, the additional force required to counteract the component of gravity along the incline is given by:
![\[ F_{\text{gravity}} = m \cdot g \cdot \sin(\theta) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/nsw0r3stqll6fpzyyskgoeu7zn3xpm34ht.png)
Given:
θ = 6 degrees
g = 9.8 m/
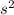
 = 2050 x 9.8 x sin 6° = 2102 N
= 2050 x 9.8 x sin 6° = 2102 N
The total force
 is the sum of the drag force and the component of gravity along the incline:
is the sum of the drag force and the component of gravity along the incline:
![\[ F_{\text{total}} = F_{\text{drag}} + F_{\text{gravity}} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/rxifkh7ph8xksqrl6bs691p7uetvbbg7a0.png) = 260 + 2102 = 2362 N
= 260 + 2102 = 2362 N
The new power
 required is then given by:
required is then given by:
![\[ P_{\text{new}} = F_{\text{total}} \cdot v \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/j08h3kx27pyy2xtn32r66wokfbmfnu5hv3.png) = 2362 x 26 = 61412 W
= 2362 x 26 = 61412 W
In horsepower,
 =
=
 = 82.3 hp
= 82.3 hp
The values vary with the angle of incline.