The enthalpy of reaction for the given chemical equation is
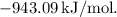
To determine the enthalpy of reaction for the given chemical equation, we need to manipulate and combine the provided equations to cancel out common compounds on both sides and obtain the target reaction:
1. **Flip and Multiply Equations:**
- Flip the first equation to match the reactants of the target reaction:
![\[ HCl(g) + NaNO_2(s) \rightarrow HNO_2(l) + NaCl(s) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/college/tomp1hza4mt8wq7lyssrz1uhze46i5jjxh.png)
Multiply this equation by 2 to match the coefficients in the target reaction.
2. **Combine Equations:**
- Combine the manipulated equation with the second equation to eliminate
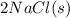 :
:
![\[ HCl(g) + NaNO_2(s) + 2NaCl(s) + H_2O(l) \rightarrow 2HCl(g) + Na_2O(s) + 2NaNO_2(s) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/college/hytkdh310nzcksank1z7kurhweszp2cjc1.png)
Multiply this equation by -1 to subtract it.
3. **Combine with Additional Equations:**
- Combine the resulting equation with the third and fourth equations to cancel out
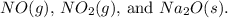
![\[ HCl(g) + NaNO_2(s) + 2NaCl(s) + H_2O(l) \rightarrow 2HNO_2(l) + N_2O(g) + O_2(g) + H_2O(l) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/college/fo8pqeqyijyv3iqop1zyl5srvbkofpgw38.png)
4. **Calculate Enthalpy:**
- Sum the enthalpies of the individual reactions to get the enthalpy of the overall reaction:
![\[ \Delta H_{\text{overall}} = \sum \Delta H_{\text{individual}} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/college/jhxlt0rhqj1rh7v09t561a1z3lnwzwlilb.png)
![\[ \Delta H_{\text{overall}} = (-507.1) + (-427.0) + (-43.01) + (+34.02) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/college/vmjrbpaoqznz9101oolhju72nrljpmx271.png)
![\[ \Delta H_{\text{overall}} = -943.09 \, \text{kJ/mol} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/college/8sawl194aic4ajnfd903ao33micixag5p0.png)