Answer:
394.68 J
Step-by-step explanation:
The amount of heat gained or lost by an object when its temperature changes can be calculated by using the formula:
Specific Heat Capacity
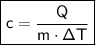
where:
- c is the specific heat of the object.
- Q is the heat gained or lost in joules (J).
- m is the mass of the object.
- ΔT is the change in temperature.
The initial temperature of the marble was 22°C and its final temperature is 45°C. Therefore, the change in temperature, ΔT, is:
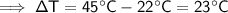
Therefore, the values to substitute into the formula are:
- m = 20.0 g
- c = 0.858 J / (g · °C)
- ΔT = (45°C - 22°C) = 23°C
Substitute these values into the formula:
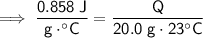
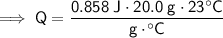
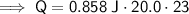
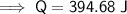
Therefore, 394.68 J of heat is required to raise the temperature of 20.0 g of marble from 22°C to 45°C.