Answer:
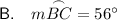
Explanation:
To find the measure of arc BC, first calculate the measures of arc ABC and arc BCD.
Definitions:
- A chord is a straight line joining two points on the circle.
- An inscribed angle is the angle formed (vertex) when two chords meet at one point on a circle.
- An intercepted arc is the arc that is between the endpoints of the chords that form the inscribed angle.
Inscribed Angle Theorem
The measure of an inscribed angle is half the measure of the intercepted arc.
Therefore, we can use the inscribed angle theorem to calculate the measures of arcs ABC and BCD:
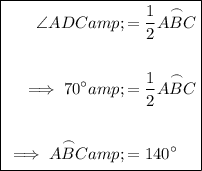
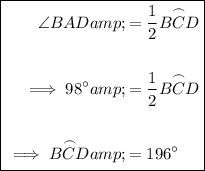
The sum of the arcs is 360°. Therefore:
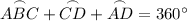
Substitute the given measure of arc AD and the found measure of arc ABC and solve for arc CD:
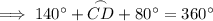
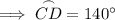
The measure of arc BCD is the sum of arcs BC and CD. Therefore:
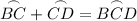
To find the measure of arc BC, substitute the found measures of arc CD and arc BCD and solve for BC:
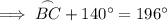
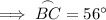
Therefore, the measure of arc BC is 56°.