Equations/Concepts Used:
Kinetic Energy =>
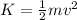
Gravitational Potential Energy =>
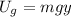
Mechanical Energy =>
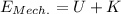
Conservation of Energy =>
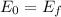
At point 1
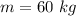
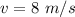
PE ==>
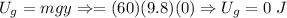
KE ==>
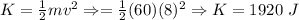
ME==>

At point 2
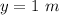
Find the velocity of the skater at point 2 using conservation of energy.
We already found the total energy at point 1, which was 1920 Joules.
==>
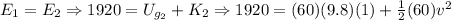
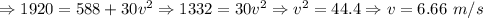
From the equation above we answered the following,
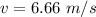
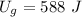
We know the velocity at point 2, find KE then ME.
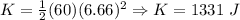
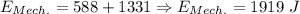
Notice how mechanical energy remains constant, this is because energy is a conserved quantity.
At point 3
Use conservation of energy again, using points 1 and 3.
==>

At point 3 the skaters velocity will go to 0 and all energy will be potential.
So,
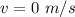
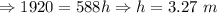
==>
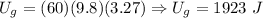
Answers:
Point 1, PE=0 J, KE=1920 J, ME=1920J
Point 2, PE=588 J, KE= 1331 J, ME= 1919 J, v=6.66 m/s
Point 3, PE=1923 J, KE=0 J ,ME= 1923 J, v=0 m/s, h=3.27 m