Answer:
The value of the derivative at (0, 0) is zero.
Explanation:
Given function:
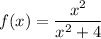
To differentiate the given function, use the quotient rule and the power rule of differentiation.



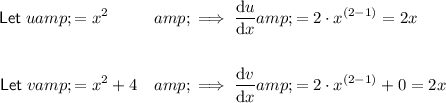
Apply the quotient rule:
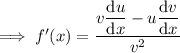
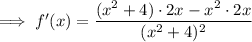
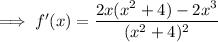
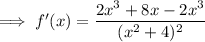
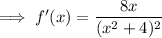
An extremum is a point where a function has a maximum or minimum value. From inspection of the given graph, the minimum point of the function is (0, 0).
To determine the value of the derivative at the minimum point, substitute x = 0 into the differentiated function.
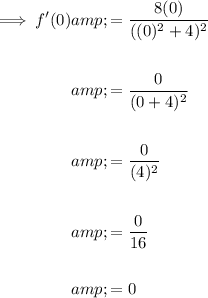
Therefore, the value of the derivative at (0, 0) is zero.