Answer:
- a = -13
- b = 6
- f(x) = (2x -1)(x -2)(x +3)
Explanation:
Given f(x) = 2x³ +x² +ax +b has a factor (x -2) and a remainder of 18 when divided by (x -1), you want to know a, b, and the factored form of f(x).
Remainder
If (x -2) is a factor, then the value of f(2) is zero:
f(2) = 2·2³ +2² +2a +b = 0
2a +b = -20 . . . . . . . subtract 20
If the remainder from division by (x +1) is 18, then f(-1) is 18:
f(-1) = 2·(-1)³ +(-1)² +a·(-1) +b = 18
-a +b = 19 . . . . . . . . . . add 1
Solve for a, b
Subtracting the second equation from the first gives ...
(2a +b) -(-a +b) = (-20) -(19)
3a = -39
a = -13
b = 19 +a = 6
The values of 'a' and 'b' are -13 and 6, respectively.
Factored form
We can find the quadratic factor using synthetic division, given one root is x=2. The tableau for that is ...
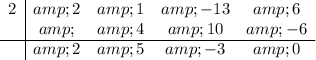
The remainder is 0, as expected, and the quadratic factor of f(x) is 2x² +5x -3. Now, we know f(x) = (x -2)(2x² +5x -3).
To factor the quadratic, we need to find factors of (2)(-3) = -6 that have a sum of 5. Those would be 6 and -1. This lets us factor the quadratic as ...
2x² +5x -3 = (2x +6)(2x -1)/2 = (x +3)(2x -1)
The factored form of f(x) is ...
f(x) = (2x -1)(x -2)(x +3)