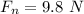Answer:
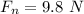
General Formulas and Concepts:
Math
Pre-Algebra
Order of Operations: BPEMDAS
- Brackets
- Parenthesis
- Exponents
- Multiplication
- Division
- Addition
- Subtraction
Physics
Forces
SI Unit: Newtons N
Free Body Diagrams
Gravitational Force:
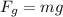
- m is mass (in kg)
- g is Earth's gravity (9.8 m/s²)
Normal Force:
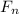
Newton's Law of Motions
- Newton's 1st Law of Motion: An object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion stays in motion
- Newton's 2nd Law of Motion: F = ma (Force is equal to [constant] mass times acceleration)
- Newton's 3rd Law of Motion: For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction
Step-by-step explanation:
Step 1: Define
1 kg book at rest
Step 2: FBD
See Attachment
Draw a free body diagram to label the forces acting upon the book. We see that we would have gravitational force from Earth pointing downwards and normal force from the surface of the desk pointing upwards.
Since the book is not moving, we know that ∑F = 0 (sum of forces equal to 0).
Step 4: Find Normal Force
- Define Forces [Newton's Law of Motions]:
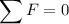
- [Newton's Law of Motions] Substitute in forces:
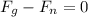
- [Newton's Law of Motions] [Addition Property of Equality] Isolate
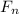 :
:
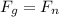
- [Newton's Law of Motions] Substitute in
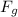 :
:
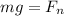
- [Newton's Law of Motions] Rewrite:
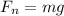
- [Newton's Law of Motions] Substitute in variables:
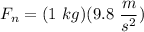
- [Newton's Law of Motions] Multiply: