Answer:
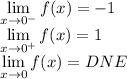
General Formulas and Concepts:
Algebra I
- Graphing Functions
- Function Notation
Calculus
Limits
- Evaluating Limits Graphically
- If
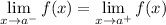 , then
, then
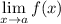 exists
exists
Explanation:
Step 1: Define
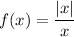
Step 2: Graph/Evaluate
Graph the function so we can evaluate the given limits. See attachment.
We see from the function that when we approach 0 from the left, we will get a -1.
∴
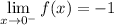
We see from the function that when we approach 0 from the right, we will get a 1.
∴
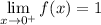
Since the limit from the left does not equal the limit from the right, the limit as x approaches 0 of f(x) does not exist (DNE).