For the given reaction the enthalpy of the reaction in which sulfur dioxide is oxidized to sulfur trioxide 2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2SO3 (g) is 100 kJ.
To determine the enthalpy change
 for the reaction in which sulfur dioxide is oxidized to sulfur trioxide:
for the reaction in which sulfur dioxide is oxidized to sulfur trioxide:
![\[2SO_2 (g) + O_2 (g) \rightarrow 2SO_3 (g)\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/college/cxbcv4lesgwqmuimnn1djnpic502r93poi.png)
you can use Hess's Law. This law states that the overall enthalpy change for a reaction is the sum of the enthalpy changes of its individual steps.
Given reactions:
1.
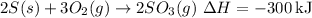
2.
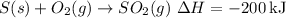
To find the enthalpy change for the target reaction, subtract the enthalpy change of the second reaction from the first:
![\[\Delta H = (-300 \, \text{kJ}) - (-200 \, \text{kJ})\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/college/nfns8hic2vn2dmceb1ci292bqc0y687j33.png)
![\[\Delta H = -300 \, \text{kJ} + 200 \, \text{kJ}\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/college/2nporc7p3j2d7rgra05bvaj2u0yzdg1ub6.png)
![\[\Delta H = -100 \, \text{kJ}\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/college/5gw74vaj07rvg9o5jxzg4siwlzs7cuf5ys.png)
So, the enthalpy change for the oxidation of sulfur dioxide to sulfur trioxide is
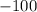 ,
,
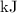 .
.