The equation f(x) =
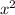 + 4 has no real solutions, but if you're working with complex numbers, the solutions are x = 2i and x = -2i.
+ 4 has no real solutions, but if you're working with complex numbers, the solutions are x = 2i and x = -2i.
To solve the equation f(x) =
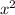 + 4, we need to find the values of x that make the equation true. Here's how you can do it:
+ 4, we need to find the values of x that make the equation true. Here's how you can do it:
1. Set f(x) equal to zero: f(x) =
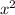 + 4 = 0.
+ 4 = 0.
2. Subtract 4 from both sides of the equation to isolate the
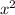 term:
term:
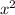 = -4.
= -4.
3. Take the square root of both sides of the equation: x = ±√(-4).
Now, when it comes to the square root of a negative number, such as -4, it's important to note that it is not a real number. In the real number system, the square root of a negative number does not exist. This means that there are no real solutions to the equation f(x) =
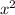 + 4.
+ 4.
However, if you're working with complex numbers, you can express the square root of -4 as ±2i, where i represents the imaginary unit (√-1). In this case, the solutions to the equation f(x) =
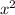 + 4 would be x = 2i and x = -2i.
+ 4 would be x = 2i and x = -2i.
In summary, the equation f(x) =
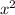 + 4 has no real solutions, but if you're working with complex numbers, the solutions are x = 2i and x = -2i.
+ 4 has no real solutions, but if you're working with complex numbers, the solutions are x = 2i and x = -2i.