The vector projection
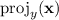 of vector
of vector
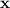 onto vector
onto vector
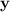 is
is
 given vectors
given vectors
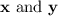 .
.
The vector projection
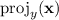 of vector
of vector
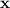 onto vector
onto vector
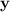 is given by:
is given by:
![\[ \text{proj}_y(\mathbf{x}) = \frac{\mathbf{x} \cdot \mathbf{y}}{\|\mathbf{y}\|^2} \cdot \mathbf{y} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/ik2qpmmti73feojhyovabnbe17j37ad2qa.png)
Given vectors
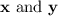 :
:
![\[ \mathbf{x} = \begin{bmatrix} -1 \\ 1 \\ -2 \end{bmatrix}, \quad \mathbf{y} = \begin{bmatrix} 3 \\ -1 \\ 4 \end{bmatrix} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/93s1d7sfctmtjlxau3vfczpj8n4f3cdhq6.png)
1. Calculate the dot product
 :
:
![\[ \mathbf{x} \cdot \mathbf{y} = (-1)(3) + (1)(-1) + (-2)(4) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/427ch1tg44869066j3kxaycyaallkhzc0d.png)
2. Calculate the norm
 of vector
of vector
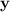 :
:
![\[ \|\mathbf{y}\| = √(3^2 + (-1)^2 + 4^2) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/4cm2t9cgkprcnpc2c4o8lvq1lpj81ux2dk.png)
3. Substitute these values into the formula:
![\[ \text{proj}_y(\mathbf{x}) = \frac{\mathbf{x} \cdot \mathbf{y}}{\|\mathbf{y}\|^2} \cdot \mathbf{y} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/ik2qpmmti73feojhyovabnbe17j37ad2qa.png)
Perform the calculations to find the vector projection.
![\[ \mathbf{x} = \begin{bmatrix} -1 \\ 1 \\ -2 \end{bmatrix}, \quad \mathbf{y} = \begin{bmatrix} 3 \\ -1 \\ 4 \end{bmatrix} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/93s1d7sfctmtjlxau3vfczpj8n4f3cdhq6.png)
1. Calculate the dot product
 :
:
![\[ \mathbf{x} \cdot \mathbf{y} = (-1)(3) + (1)(-1) + (-2)(4) = -3 - 1 - 8 = -12 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/tzh97sqy4wbggrqv9ep9z99d08qts6vq2w.png)
2. Calculate the norm
 of vector
of vector
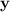 :
:
![\[ \|\mathbf{y}\| = √(3^2 + (-1)^2 + 4^2) = √(9 + 1 + 16) = √(26) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/vii5bxahgqueu3no3qs4yxzvnxueme7bqw.png)
3. Substitute these values into the formula:
![\[ \text{proj}_y(\mathbf{x}) = \frac{\mathbf{x} \cdot \mathbf{y}}{\|\mathbf{y}\|^2} \cdot \mathbf{y} \]\[ \text{proj}_y(\mathbf{x}) = (-12)/(26) \cdot \begin{bmatrix} 3 \\ -1 \\ 4 \end{bmatrix} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/nnw2caqa4hhkluxnkuilgc6cr9uag9flmo.png)
4. Perform the calculation:
![\[ \text{proj}_y(\mathbf{x}) = -(6)/(13) \cdot \begin{bmatrix} 3 \\ -1 \\ 4 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} -(18)/(13) \\ (6)/(13) \\ -(24)/(13) \end{bmatrix} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/h8xkfhnbf4b3o6gewsnpizuxj8bx5puyic.png)
Therefore, the vector projection
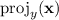 of vector
of vector
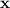 onto vector
onto vector
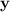 is
is
 .
.