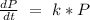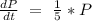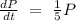Answer:
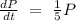
Explanation:
Given
Variation: Directly Proportional
Insects = 10 million when Rate = 2 million
i.e.
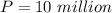 when
when
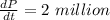
Required
Determine the differential equation for the scenario
The variation can be represented as:
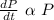
Which means that the rate at which the insects increase with time is directly proportional to the number of insects
Convert to equation
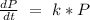
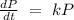
Substitute values for
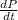 and P
and P
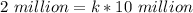
Make k the subject
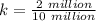
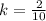
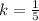
Substitute
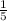 for k in
for k in