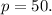Final Answer:
The price per unit when the quantity demanded is half of the original demand
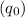 is given by
is given by
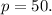
Step-by-step explanation:
The given demand function is
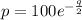 , where
, where
 is the price per unit and
is the price per unit and
 is the number of units.
is the number of units.
To find the price per unit when the quantity demanded is half of the original demand
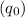 , set
, set
 in the demand function and solve for
in the demand function and solve for

![\[p = 100e^{-(1)/(2)\cdot(q_0)/(2)}\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/business/college/p5qi6vl4p3vsjhl5bk6tue6e9rkarmtray.png)
Simplifying this expression gives:
![\[p = 100e^{-(q_0)/(4)}\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/business/college/tabxxw7uvmwkg049xtz4om3dunr6g1bsl6.png)
Now, since
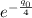 is the same as
is the same as
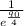 , we can rewrite the expression as:
, we can rewrite the expression as:
![\[p = \frac{100}{e^{(q_0)/(4)}}\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/business/college/fmurdib6tcg2t7p5cyruw5uczhvfrdmxnq.png)
Now, when
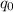 is substituted by
is substituted by
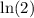 (since half of the original demand corresponds to
(since half of the original demand corresponds to
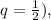 we get:
we get:
![\[p = (100)/(e^(\ln(2)/4))\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/business/college/rh0lo94ilb4fw7kefrjgr7e6x0owejo2ff.png)
Simplifying further gives:
![\[p = \frac{100}{\sqrt[4]{2}}\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/business/college/g4bsj5c671ufe4dnydizj5moq0avtvdukc.png)
![\[p = 50\]\alpha](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/business/college/kex7qu2nz1sj6s9s40cuqtw1o6nraewj7c.png)
Therefore, the price per unit when the quantity demanded is half of the original demand is