9514 1404 393
Answer:
9. a = 3, b = 3, y-intercept = 3
10. a = 5, b = 0.6, y-intercept = 5
Explanation:
The picture is fuzzy, but we think the given equations are ...
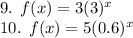
You are comparing these to the form ...
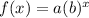
so the values of 'a' and 'b' should be readily identifiable. The y-intercept in each case is y = a.
The end behavior depends on whether b > 1 or not. Growth functions (b>1) go to 0 on the left and ∞ on the right. Decay functions (b<1) are the reverse.
__
9. a = 3, b = 3, y-intercept = 3
The end behaviors are (x, f(x)) ⇒ (-∞, 0), (∞, ∞).
__
10. a = 5, b = 0.6, y-intercept = 5
The end behaviors are (x, f(x)) ⇒ (-∞, ∞), (∞, 0).