Answer:
The required acceleration is
 m/s²
m/s²
Step-by-step explanation:
Given
To determine
Acceleration a = ?
We know that acceleration is produced when a force is applied to a body.
The acceleration can be determined using the formula
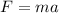
where
now substituting F = 250 , and m = 221 in the formula
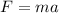
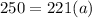
switch the equation
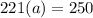
Divide both sides by 221
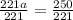
simplify
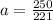
 m/s²
m/s²
Therefore, the required acceleration is
 m/s²
m/s²