The probability that 0 will not be reached in
 steps approaches
steps approaches
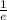 or approximately 0.3679.
or approximately 0.3679.
If the estimated number of steps needed to reach 0 from n is
 , it implies that the probability of not reaching 0 within
, it implies that the probability of not reaching 0 within
 steps can be determined.
steps can be determined.
Let's consider the probability of not reaching 0 in a single step from a specific n to n−1. This probability is
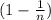 because there's only one way to reach n−1 (by decrementing from n), out of n possible numbers (including 0).
because there's only one way to reach n−1 (by decrementing from n), out of n possible numbers (including 0).
Now, for n steps, the probability of not reaching 0 is
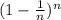
This can be thought of as the probability of not reaching 0 in a single step, repeated n times.
For
 steps, the probability of not reaching 0 is
steps, the probability of not reaching 0 is
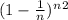
This probability tends to
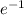 (where e is the base of the natural logarithm) as n becomes large.
(where e is the base of the natural logarithm) as n becomes large.
So, the probability that 0 will not be reached in n^2 steps approaches
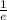 or approximately 0.3679.
or approximately 0.3679.