Final Answer:
The net present value (NPV) of the project cannot be determined without information about the discount rate.
Step-by-step explanation:
To evaluate the financial attractiveness of the project, the net present value (NPV) needs to be calculated. NPV is computed by discounting the expected free cash flows at a given discount rate. The formula for NPV is as follows:
![\[ NPV = \sum_(t=1)^(T) (CF_t)/((1 + r)^t) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/business/high-school/meute2szwxq6p9f66kdjijs3ufbnfobj0o.png)
where \(CF_t\) is the cash flow in year \(t\), \(r\) is the discount rate, and \T is the total number of years.
In this case, the expected free cash flows are given for each year
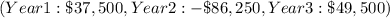 . However, the net present value cannot be determined without knowing the discount rate r. The discount rate is a crucial factor as it reflects the time value of money and the required rate of return for the investment. Without this rate, we cannot calculate the present value of the future cash flows, and therefore, the NPV remains unknown.
. However, the net present value cannot be determined without knowing the discount rate r. The discount rate is a crucial factor as it reflects the time value of money and the required rate of return for the investment. Without this rate, we cannot calculate the present value of the future cash flows, and therefore, the NPV remains unknown.
In financial decision-making, a positive NPV indicates that the project is expected to generate value and is considered favorable, while a negative NPV suggests the opposite. Determining the NPV allows companies to assess the profitability of an investment and make informed decisions about whether to proceed with the project.