Final Answer:
The kinetic energy KE formula for an object with mass m traveling at velocity v is given by
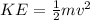 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
The kinetic energy of an object is a fundamental concept in physics, representing the energy it possesses due to its motion. The formula
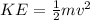 describes this energy, where m is the mass of the object and v is its velocity. The factor
describes this energy, where m is the mass of the object and v is its velocity. The factor
 is crucial, as it originates from the work-energy principle and is a result of integrating the force applied to the object with respect to displacement.
is crucial, as it originates from the work-energy principle and is a result of integrating the force applied to the object with respect to displacement.
Breaking down the formula,
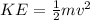
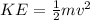 shows that the kinetic energy is directly proportional to the square of the velocity and the mass of the object. This means that an increase in either velocity or mass will result in a proportional increase in kinetic energy. This formula is applicable across various contexts, from calculating the energy of a moving vehicle to understanding the energetic aspects of microscopic particles.
shows that the kinetic energy is directly proportional to the square of the velocity and the mass of the object. This means that an increase in either velocity or mass will result in a proportional increase in kinetic energy. This formula is applicable across various contexts, from calculating the energy of a moving vehicle to understanding the energetic aspects of microscopic particles.
Understanding kinetic energy is vital in physics and engineering, aiding in the analysis and design of systems involving moving objects. Whether in mechanics, thermodynamics, or other branches of physics, the kinetic energy formula provides a quantitative measure of the energy associated with the motion of an object, contributing to a comprehensive understanding of dynamic systems.