To convert a linear equation from standard form to slope-intercept form, which is in the form
 , where
, where
 is the slope and
is the slope and
 is the y-intercept, follow below steps.
is the y-intercept, follow below steps.
To convert a linear equation from standard form to slope-intercept form, which is in the form
 , where
, where
 is the slope and
is the slope and
 is the y-intercept, we can follow these steps:
is the y-intercept, we can follow these steps:
1. Standard Form of a Linear Equation:
Standard form looks like this:
 , where
, where
 are constants, and
are constants, and
 is usually a positive integer.
is usually a positive integer.
2. Isolate
 :
:
Our goal is to get the equation in the form
 , so isolate
, so isolate
 on one side of the equation. If the equation is in the standard form
on one side of the equation. If the equation is in the standard form
 , subtract
, subtract
 from both sides.
from both sides.
Example:
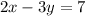
![\[ -3y = -2x + 7 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/vzw6h5d6p9zk331sph5ycy9yok2sywyyk1.png)
3. Divide by the Coefficient of
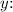
Once
 is on one side, divide both sides by the coefficient of
is on one side, divide both sides by the coefficient of
 to make it 1.
to make it 1.
Example:
![\[y = (2)/(3)x - (7)/(3)\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/v8q4186ni0owbmizcbvss35lr8y74ktwop.png)
4. Adjust the Form:
If needed, rearrange the equation to make it look more like
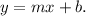
Example:
![\[y = (2)/(3)x - (7)/(3)\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/v8q4186ni0owbmizcbvss35lr8y74ktwop.png)
Multiply through by 3 to clear the fraction:
![\[3y = 2x - 7\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/lva4c7d04shpsbb2fw36hcvojpj7nuo2qq.png)
The final slope-intercept form is
 .
.
The probable question may be:
"How to convert standard form to slope intercept form?"