Final answer:
The INR level that is considered a contraindication for tPA administration is 1.7.
Step-by-step explanation:
The International Normalized Ratio (INR) is a standardized measure of blood clotting time. For tPA (tissue plasminogen activator) administration in conditions such as ischemic stroke, an INR level greater than 1.7 is generally considered a contraindication. This is because a higher INR indicates an increased risk of bleeding, and tPA, which is a thrombolytic agent, further elevates this risk. The rationale behind this threshold is to balance the potential benefits of clot dissolution with the risk of excessive bleeding.
To calculate the INR, it's first necessary to find the patient's prothrombin time (PT) and the control PT. The formula for INR is INR = (Patient PT / Control PT)^ISI, where ISI (International Sensitivity Index) is a calibration factor for the specific thromboplastin reagent used. For example, if the patient's PT is 14 seconds and the control PT is 11 seconds, and the ISI is 2, then INR =
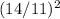 = 1.69. In this case, an INR of 1.69 is below the contraindication threshold, and tPA administration may be considered.
= 1.69. In this case, an INR of 1.69 is below the contraindication threshold, and tPA administration may be considered.
Maintaining an INR within the recommended range is crucial in preventing complications, as an elevated INR signifies an increased risk of bleeding. Clinicians carefully assess these values before deciding to administer tPA, ensuring patient safety and optimizing treatment outcomes.