Kinetic energy in electrons is a result of their motion, described by classical physics and extended through quantum mechanics, impacting various scientific and technological domains.
In the context of electrons, kinetic energy is a manifestation of the energy associated with the motion of these subatomic particles. According to classical physics, the kinetic energy (KE) of an electron is calculated using the equation
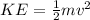 , where m represents the mass of the electron and v is its velocity. In this equation, the squared velocity term highlights the significance of the speed of the electron in determining its kinetic energy.
, where m represents the mass of the electron and v is its velocity. In this equation, the squared velocity term highlights the significance of the speed of the electron in determining its kinetic energy.
As electrons move within an atom or in a conducting material, they exhibit varying velocities depending on their energy levels or the potential difference across a circuit. In the realm of quantum mechanics, where the wave-particle duality of electrons is considered, the concept of kinetic energy is extended to incorporate the de Broglie wavelength, linking the momentum of electrons to their wave properties.
Understanding and manipulating the kinetic energy of electrons is crucial in fields such as semiconductor physics and electronics, where electron mobility and behavior influence device performance. Moreover, in phenomena like photoelectric effect or electron emission, the energy of emitted electrons is directly related to their kinetic energy, providing insights into the quantum nature of particles.
The question probable may be:
How is kinetic energy manifested in the context of electrons?