Answer:
1
Explanation:
The net change in a function over a specified interval is the difference between its final and initial values, representing the overall shift or variation in the function across that interval.
To find the net change in h between x = -3 and x = 3, begin by finding the values of h(x) at those points on the graph:
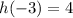

Calculate the net change by subtracting the initial value h(-3) from the final value h(3).
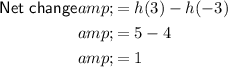
Therefore, the net change of h between x = -3 and x = 3 is 1.
This means that the function h(x) increases by 1 unit between x = -3 and x = 3.