The left electrode will be positive due to the lower concentration in the left half-cell. The exact voltage depends on the standard cell potential, which is not provided.
The electrode that will be positive in this galvanic cell is the left electrode. The left half-cell has a lower concentration of
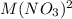 , specifically a 350. mM solution, compared to the right half-cell's 3.50 M solution. According to the Nernst equation, as the concentration of the metal ion in the half-cell decreases, the cell potential increases, making the left electrode positive.
, specifically a 350. mM solution, compared to the right half-cell's 3.50 M solution. According to the Nernst equation, as the concentration of the metal ion in the half-cell decreases, the cell potential increases, making the left electrode positive.
The Nernst equation is given by:
![\[ E = E^\circ - \left( (RT)/(nF) \right) \ln \left( ([M^2+])/([M^2+]) \right) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/college/7gmvdyogruhzg5t2iku1apvcm9k94nbeab.png)
Where:
 is the cell potential,
is the cell potential,
 is the standard cell potential,
is the standard cell potential,
 is the ideal gas constant (8.314 J/(mol·K)),
is the ideal gas constant (8.314 J/(mol·K)),
 is the temperature in Kelvin,
is the temperature in Kelvin,
 is the number of moles of electrons transferred in the reaction,
is the number of moles of electrons transferred in the reaction,
 is Faraday's constant (96,485 C/mol),
is Faraday's constant (96,485 C/mol),
![\([M^2+]\)](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/college/z17nefof92hxpo6u7kxfmh4kitoqrurjar.png) is the concentration of
is the concentration of
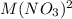 in the left half-cell,
in the left half-cell,
![\([M^2+]\)](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/college/z17nefof92hxpo6u7kxfmh4kitoqrurjar.png) is the concentration of
is the concentration of
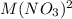 in the right half-cell.
in the right half-cell.
Given the conditions and concentrations, the left electrode will be positive.
As for the voltage displayed on the voltmeter, without specific values for the standard cell potential
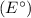 , it's challenging to provide an exact voltage. However, the voltmeter would show a positive value, reflecting the higher cell potential due to the lower concentration in the left half-cell. The exact value would require more information, such as the standard cell potential.
, it's challenging to provide an exact voltage. However, the voltmeter would show a positive value, reflecting the higher cell potential due to the lower concentration in the left half-cell. The exact value would require more information, such as the standard cell potential.