Answer: 0.101
Step-by-step explanation:
Using the fact that molarity = (moles of solute)/(liters of solution), there are
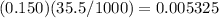 moles of barium hydroxide.
moles of barium hydroxide.
There are 2 moles of hydroxide ions per mole of barium hydroxide, meaning that there are
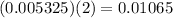 moles of hydroxide ions.
moles of hydroxide ions.
To neutralize the solution, the number of moles of hydrogen ions must be equal to the number of moles of hydroxide ions.
Since there is 1 mole of hydrogen ions per mole of nitric acid, we need 0.01065 moles of nitric acid.
Substituting into the molarity formula yields that the concentration is
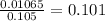 M.
M.