Answer:
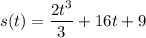
General Formulas and Concepts:
Pre-Algebra
Order of Operations: BPEMDAS
- Brackets
- Parenthesis
- Exponents
- Multiplication
- Division
- Addition
- Subtraction
Calculus
Antiderivatives - Integrals
Integration Constant C
Integration Rule [Reverse Power Rule]:
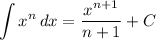
Integration Property [Multiplied Constant]:
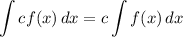
Integration Property [Addition/Subtraction]:
![\displaystyle \int {[f(x) \pm g(x)]} \, dx = \int {f(x)} \, dx \pm \int {g(x)} \, dx](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/r5yh324r81plt97j3zrr5qi2xxczxlqi34.png)
Explanation:
*Note:
Velocity is the derivative of Position, and Acceleration is derivative of Velocity.
↓
Velocity is integration of Acceleration, Position is integration of Velocity.
Step 1: Define
a(t) = 4t m/s²
s(0) = 9 m
v(0) = 16 m/s
Step 2: Find Velocity Function
Integration Pt. 1
- [Velocity] Set up integral:
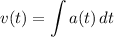
- [Velocity] Substitute in function:
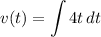
- [Velocity] Rewrite [Integration Property - Multiplied Constant]:
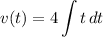
- [Velocity] Integrate [Integration Rule - Reverse Power Rule]:
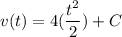
- [Velocity] Multiply:
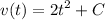
Finding C
- [Velocity] Substitute in initial condition:
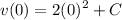
- [Velocity] Substitute in function value:
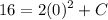
- [Velocity] Evaluate exponents:
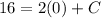
- [Velocity] Multiply:
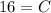
- Rewrite:
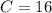
Velocity Function:
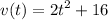
Step 3: Find Position Function
Integration Pt. 2
- [Position] Set up integral:
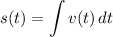
- [Position] Substitute in function:
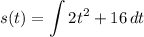
- [Position] Rewrite [Integration Property - Addition]:
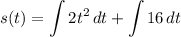
- [Position] Rewrite [Integration Property - Multiplied Constant]:
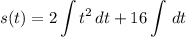
- [Position] Integrate [Integration Rule - Reverse Power Rule]:
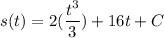
- [Position] Multiply:
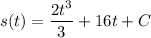
Finding C
- [Position] Substitute in initial condition:
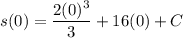
- [Position] Substitute in function value:
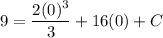
- [Position] Evaluate exponents:
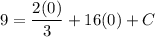
- [Position] Multiply:
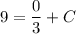
- [Position] Divide:
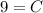
- [Position] Rewrite:
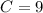
Position Function:
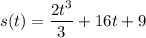
Topic: AP Calculus AB/BC (Calculus I/II)
Unit: Integration
Book: College Calculus 10e