Final Answer:
1. The probability that the entire 20-bit frame has no errors during transmission is
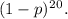
2. The probability of a single bit being in error during the transmission process is
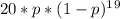 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
1. The probability of no errors in a single bit transmission is (1-p). Since there are 20 bits in the frame, the probability of the entire frame being error-free is
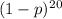 .
.
2. To find the probability of a single bit being in error during the transmission process, we consider that any one of the 20 bits could be in error. Therefore, we multiply the probability of a single bit being in error (p) by the probability of the remaining 19 bits being error-free
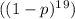 . The expression for this is
. The expression for this is
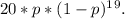
In summary, for the first part, the probability that the entire 20-bit frame has no errors is simply the product of the individual probabilities of each bit being error-free. For the second part, we consider the probability of a single bit being in error and multiply it by the probability of the remaining bits being error-free. These calculations are based on the assumption that errors in different bits are independent events.