Final answer:
The speed of a particle is the magnitude of the velocity vector. As an example, given the velocity function
 , the speed at
, the speed at
 would be calculated as
would be calculated as
 . It's crucial to provide the units which, in this context, are meters per second (m/s).
. It's crucial to provide the units which, in this context, are meters per second (m/s).
Step-by-step explanation:
To determine the speed of a particle at distance d, you need to have a specific function that relates speed, distance, or time. In general, speed is a scalar quantity that represents how fast a particle is moving, regardless of its direction of travel. It is the magnitude of the velocity vector and is given by the equation:
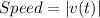
For instance, given a velocity function
 , you can calculate the speed at a specific time by taking the absolute value of the velocity. Substituting t = 2.0 s into the equation:
, you can calculate the speed at a specific time by taking the absolute value of the velocity. Substituting t = 2.0 s into the equation:
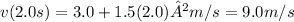
Thus, the speed of the particle at
 It's important to express the answer with the appropriate units, which in this case is meters per second (m/s). Similarly, for other given functions or scenarios, you follow the same process to calculate the speed at a particular instance based on the provided formula for velocity or position as a function of time.
It's important to express the answer with the appropriate units, which in this case is meters per second (m/s). Similarly, for other given functions or scenarios, you follow the same process to calculate the speed at a particular instance based on the provided formula for velocity or position as a function of time.