The work done in the reaction of 1 mole of Fe with CO to produce
 at 50°C is approximately 7968.54 Joules, assuming ideal gases and using the ideal gas law.
at 50°C is approximately 7968.54 Joules, assuming ideal gases and using the ideal gas law.
To calculate the work done in the reaction of 1 mole of Fe with CO to produce
 at 50°C, we can use the ideal gas law and the equation for work done.
at 50°C, we can use the ideal gas law and the equation for work done.
The ideal gas law is given by:
![\[ PV = nRT \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/college/a99uftpldttp3mar5rusl3q2cnjbrkvv83.png)
Where:
 is the pressure,
is the pressure,
 is the volume,
is the volume,
 is the number of moles,
is the number of moles,
 is the ideal gas constant (8.314 J/(mol·K)),
is the ideal gas constant (8.314 J/(mol·K)),
 is the temperature in Kelvin.
is the temperature in Kelvin.
The work done
 can be calculated using the equation:
can be calculated using the equation:
![\[ W = -\Delta nRT \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/college/78bfmjzioe6o6xpgq7l21n844vq59ysbxz.png)
Where:
 is the change in the number of moles of gas (product moles - reactant moles).
is the change in the number of moles of gas (product moles - reactant moles).
The balanced chemical equation shows that 1 mole of Fe reacts with 4 moles of CO to produce 1 mole of
 . Therefore,
. Therefore,
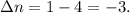
Now, substituting the values into the work equation:
![\[ W = -(-3) * 8.314 \, \text{J/(mol·K)} * (50 + 273.15) \, \text{K} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/college/k5yfw0vvisysitmjn4o095annyxmn3ituc.png)
![\[ W \approx 3 * 8.314 * 323.15 \, \text{J} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/college/4twytl4z31qsf6js37ao0b9pb6vc67cdpe.png)
![\[ W \approx 7968.542 \, \text{J} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/college/jlogd1sc8yy68601yd12srklxrbhq3ub31.png)
Therefore, the work done in the reaction is approximately 7968.54 Joules.