The acceleration of the box while on the rough surface is 0.857
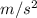 .
.
To calculate the acceleration of the box on the rough surface, Newton's second law is applied, expressed as Force = Mass x Acceleration. Given an applied force of 12 N and a box mass of 14 kg, the equation is rearranged to find acceleration. Solving for acceleration yields 0.857
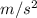 .
.
This result indicates that for every kilogram of mass, the box experiences an acceleration of approximately 0.857 meters per second squared due to the applied force. Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity, and in this context, it represents how the box's speed changes on the rough surface under the influence of the applied force.
The value of 0.857
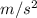 quantifies this change in velocity per unit of time, providing a numerical measure of the box's response to the force applied.
quantifies this change in velocity per unit of time, providing a numerical measure of the box's response to the force applied.
The probable question may be:
X A 14 kg box is being pushed across a floor with an applied force of 12 N at a * constant velocity of 6 m/s. The surface then becomes very rough, and with the same applied force, the box comes to rest in 2 seconds. Calculate the acceleration of the box while on the rough surface.