A system of linear inequalities represented by the graph include:
Inequality 1: y ≥ -3/4(x) + 2
Inequality 2: y ≤ 2x - 3.
In Mathematics and Geometry, the point-slope form of a straight line can be calculated by using the following mathematical equation (formula):
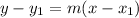
Where:
- x and y represent the data points.
- m represent the slope.
First of all, we would determine the slope of the downward sloping line by using these points (4, -1) and (0, 2);
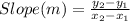
Slope (m) = (2 + 1)/(0 - 4)
Slope (m) = -3/4
At data point (0, 2) and a slope of -3/4, an equation for this line can be calculated by using the point-slope form as follows:
y - 2 = -3/4(x - 0)
y = -3/4(x) + 2
y ≥ -3/4(x) + 2 (since the solid line is shaded above)
For the the slope of the upward sloping line, we have;
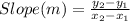
Slope (m) = (1 - 3)/(2 - 3)
Slope (m) = 2/1 = 2
At data point (2, 1) and a slope of 2, an equation for this line can be calculated by using the point-slope form as follows:
y - 1 = 2(x - 2)
y = 2x - 3
y ≤ 2x - 3 (since the solid line is shaded below)