Answer:
- NH₃ is the limiting reactant.
- Theoretical yield = 120 kg
Step-by-step explanation:
- 2NH₃ (aq) + CO₂ (aq) → CH₄N₂O (aq) + H₂O (l)
First we convert the given masses of reactants to moles, using their respective molar masses:
- 68.2 kg NH₃ ÷ 17 kg/kmol = 4.01 kmol NH₃
- 105 kg CO₂ ÷ 44 kg/kmol = 2.39 kmol CO₂
2.39 kmol of CO₂ would react completely with (2.39 * 2) 4.78 kmol of NH₃. There are not as many NH₃ kmoles so NH₃ is the limiting reactant.
We calculate how much urea would form with a 100% yield, using the moles of limiting reactant:
- 4.01 kmol NH₃ *
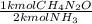 = 2.00 kmol CH₄N₂O
= 2.00 kmol CH₄N₂O
We convert that amount to kg:
- 2.00 kmol CH₄N₂O * 60 kg/kmol = 120 kg CH₄N₂O
Finally we calculate the percent yield:
- 87.5 kg / 120 kg * 100% = 72.9 %